Unresponsive apps
We’ve all been there – you are working on your computer, and suddenly, an application freezes. Not only is it frustrating, you can also end up being unsure of what to do next. Dealing with unresponsive apps on Windows can be a common yet annoying experience. However, there are several methods to resolve this issue and regain control of your system.
Note
For the purpose of this blog let us assume the application “notepad” is not responding.
Let us explore the following methods:
- Close the application the normal way
- Close the application by pressing Alt + F4
- Close the application with task manager
- Close the application with end task on the taskbar
- Close the application using the command prompt
- Close the application using power shell
- Close the application by rebooting the system
Close the application the normal way
When faced with an unresponsive application, the first step is to try to close it using the traditional method. This involves clicking on the “X” button in the application’s window or using the “Close” option from the application’s menu. If the application is still unresponsive after a few moments, we try another way.
Since everyone closes apps the normal way I guess we do not need screenshots to clarify this method.
Close the application by pressing ALT + F4
Make sure the application you want to close is in focus. This means it has to be the active window on your screen. Simultaneously press and hold the “Alt” key on your keyboard and then press the “F4” key. This key combination is a shortcut to close the active window or application. You may or may not receive a confirmation prompt before the application closes. If prompted, confirm the action to close the application.
For laptop users, depending on your keyboard layout, you may need to press the Fn key as well.
Close the application with Task Manager
There are three ways to access the Task Manager.
Press “Ctrl + Shift + Esc”.
You can press “Ctrl + Alt + Delete” and then select “Task Manager” from the menu. You navigate this menu with the arrow keys up and down. Select Task Manager and press Enter.
Type Task Manager in the search bar and select Task Manager.
Once in the Task Manager, navigate to the “Processes” tab in the left pane.
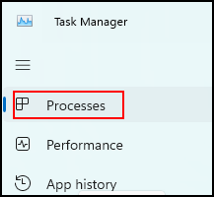
Next, locate the unresponsive application, in this example notepad, in the left pane.

Click the unresponsive application, and select End task in the top bar.
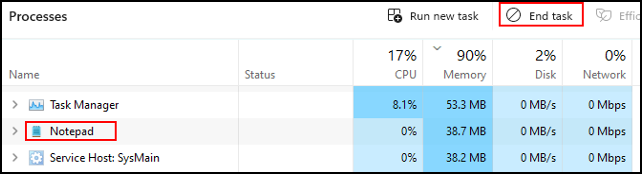
Another option is to right click the application and select end task from the context menu.
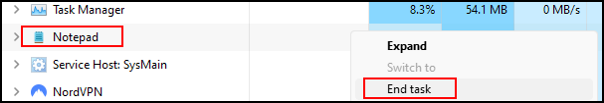
This will forcefully terminate the application and free up system resources.
Close the application with “end task” on the task bar
This option is not enabled by default.
Let us first take a look at the default situation.
Locate the app in the Taskbar and right click it.
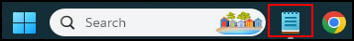
As you can see there is no option to end the app.

You have to change a setting in the system settings for the “end task” to appear when you right-click the application in the taskbar.
Here are the steps to enable this option.
Type Settings in the search bar.
![]()
Click Settings System in the context menu.
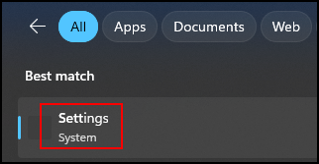
Click “System” in the left pane, the Settings screen opens.
In the left pane, click System.
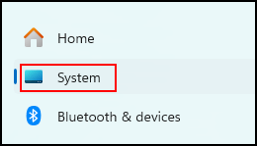
In the right pane, scroll down and click “For Developers”.
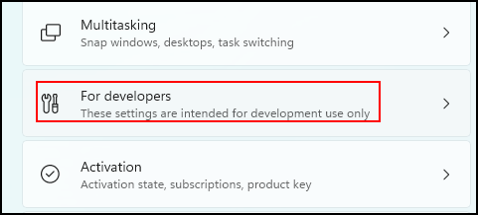
As you see the “End Task” function is set to Off.
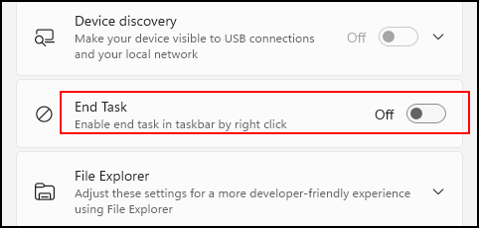
Switch the button “End Task” to On.
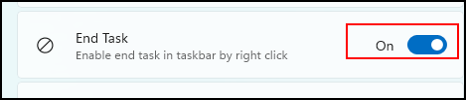
Now the settings are correct.
Now, when right click the notepad icon in the Taskbar, you will see the “End task” option.
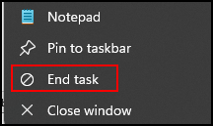
You can now use this option if your application stops to respond.
Close the application using the command prompt
You can also close programs through the command line. For this to work you have to know what the name of the program is in Windows. For notepad that is not too difficult, the name of the aplication is notepad.exe.
Type cmd in the search bar, and select “Command Prompt”.
In the screen that opens, type:
taskkill /IM notepad.exe /F
Next, press Enter
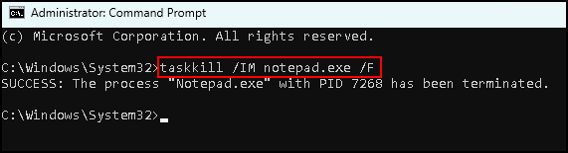
The system responds with the message that the program is terminated.
Close the application using Power Shell
Another method that can be used is the Windows PowerShell, a powerful command-line interface. Like the command prompt, you have to know the name of the application you want to close.
Type powershell in the search bar, and click Windows PowerShell.
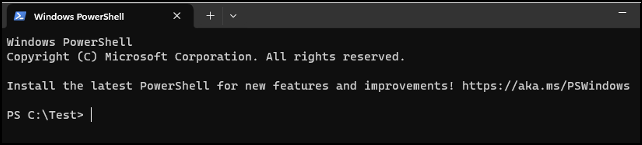
In the screen that opens, type:
Stop-Process -Name notepad
Next, press Enter
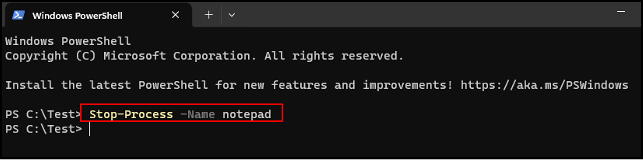
And the application notepad is closed.
Close the application by rebooting the system
In more severe cases, where an unresponsive application is causing system-wide issues, a system reboot may be necessary to regain control. When you restart your computer, any unresponsive applications are forcibly closed. This allows you to start afresh without the burden of frozen processes.
Sometimes the unresponding application is causing so many problems that even shutdown is not an option anymore. In cases like that the solution is to press and hold the power button for 5 – 10 seconds.
Conclusion
In conclusion, dealing with unresponsive apps on Windows can be a frustrating experience, but armed with the knowledge of how to end them, you can regain control of your system. Whether through the Task Manager, Windows PowerShell, or a system reboot, there are several methods to tackle unresponsive applications and ensure a smooth computing experience.
This is the end of my post on unresponsive apps.
Thank you for taking the time to read my post on unresponsive apps.
I hope you found it enjoyable and insightful.
Stay tuned for more content that is coming soon.
If you like what you read, please consider sharing it with others who might find it helpful.
Disclaimer
All tips and methods mentioned in this blog are tested on Windows 11. Please note that results may vary on other operating systems or versions of Windows. Adapt the instructions accordingly.
Copyright
© 2024 Henny Staas/safecomputer.org. Unauthorized use and/or duplication of this material without express and written permission from this site’s author and/or owner is strictly prohibited. Excerpts and links may be used, provided that full and clear credit is given to Henny Staas/safecomputer.org with appropriate and specific direction to the original content.