Browsers and passwords
In my previous posts on passwords and longer passwords, I talked about the importance of long and strong passwords. I also talked about password managers. In this post, browsers and passwords, I will discuss how browsers can create and store these passwords for you.
Many modern web browsers offer the functionality to generate, and store, secure passwords. When you create an account or change a password on a website, browsers like Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Safari, and Microsoft Edge can generate strong, random passwords for you. This feature typically appears as an option when you are prompted to create a new password or update an existing one.
Browser-generated passwords are complex and unique, and consist of a combination of letters (both uppercase and lowercase), numbers, and special characters. Generating passwords in this way enhances security by creating strong credentials that are less susceptible to brute force attacks or dictionary based password cracking methods.
Furthermore, browser-generated passwords are often stored securely within the browser’s password manager. This allows you to access and manage them alongside your other saved login credentials. This helps you maintain a higher level of security across your various online accounts without the hassle of remembering or manually creating complex passwords for each site.
Advantages
Storing passwords in web browsers can offer several conveniences and benefits for you. Firstly, it enhances efficiency and saves time by automatically filling in login credentials for frequently visited websites. This eliminates the need to manually enter usernames and passwords every time, streamlining the login process and reducing the likelihood of errors. Additionally, as mentioned earlier, browser-based password storage can enhance security.
Moreover, with browser-based password managers, you can access your saved passwords across multiple devices, allowing for seamless login experiences on smartphones, tablets, and desktop computers. This synchronization ensures consistency and accessibility, regardless of the device being used.
Furthermore, modern browsers typically employ robust encryption methods to protect stored passwords, adding an extra layer of security. Advanced security features such as biometric authentication (like fingerprint or facial recognition) can also be used to access stored passwords, further enhancing protection against unauthorized access.
Overall, storing passwords in browsers offers a convenient, efficient, and secure solution for managing login credentials, simplifying the online experience while prioritizing your security. However, it is essential that you employ additional security measures such as enabling two-factor authentication and regularly updating passwords to further safeguard your online accounts.
Disadvantages
There are also some potential disadvantages to consider.
Security risks
Storing passwords in browsers could pose a security risk if someone gains unauthorized access to your device or browser. Browsers typically encrypt your stored passwords. But, there is still a potential risk if a hacker gains access to your browser’s password manager or if your device is compromised.
Limited functionality
Browser-based password managers may lack some advanced features compared to standalone password manager applications. For example, they might not offer comprehensive security auditing, password sharing options, or secure password sharing across different platforms.
Cross platform compatability
While many browsers offer synchronization of stored passwords across devices, this functionality might be limited to specific browser ecosystems (as Chrome sync for Google Chrome users). This could be inconvenient if you use different browsers on different devices or if you switch between operating systems.
Vendor lock-in
Depending solely on a browser’s password manager could lead to vendor lock-in, where you become dependent on a specific browser for managing your passwords. Switching to a different browser or platform may require transferring your passwords manually or using third-party tools, which can be cumbersome.
Privacy concerns
You may have privacy concerns about storing sensitive login credentials within your browser, especially if you are uncomfortable with the browser’s data collection practices or if you are using a shared or public computer.
Limited integration
Browser-based password managers may not integrate seamlessly with certain websites or applications, leading to compatibility issues or difficulties in auto-filling login forms correctly.
Risk of data loss
While browser-based password managers generally offer backup and synchronization features, there is still a risk of data loss if something goes wrong with the synchronization process or if you accidentally delete stored passwords without a backup.
Conclusion
It is essential to weigh the potential disadvantages against the benefits. Consider your specific needs and preferences when deciding whether to use a browser’s built-in password management features. In many cases, combining browser-based password management with additional security measures, such as two-factor authentication and regular password updates, can help mitigate these risks.
Protect yourself against phishing
Cybercriminals are well aware that people are increasingly using complex passwords to secure their accounts. Instead of attempting to crack these passwords, hackers have found it more effective to simply ask for them. By obtaining lists of email addresses, which are readily available for purchase on the internet, hackers can launch mass email campaigns targeting these addresses.
A common tactic is to send emails which appear to come from the official government. These emails contain links to fake login pages for password changes or account maintenance. They often use stories of failed login attempts or account security breaches. The idea is to cause panic and ask for immediate action.
In the modern age, these fraudulent emails closely mimic official correspondence. They use language and formatting that closely resemble genuine communications. It has become increasingly difficult for recipients to recognize the authenticity of these messages.
It is important to never access login pages through links provided in emails. Should you receive an email containing a link, do not click on it. In the event that the email appears to be from your bank, always navigate to your bank’s official website through your usual, trusted methods. If you typically use a shortcut, continue to do so. Under no circumstances should you follow links from emails. Instead, consider contacting your bank directly via a phone call, using the established phone number stored in your device, rather than the number provided in the email.
Guarding against keyloggers
Hackers use another method to obtain passwords by secretly installing keyloggers on the computers of their victims. These programs silently capture and store all keystrokes made on the keyboard, subsequently transmitting this sensitive information to the hacker. Importantly, keyloggers do not materialize on a computer spontaneously; rather, they must be deliberately installed.
Therefore, it is important to never grant access to your computer to other individuals under any circumstances. Regardless of the strength and complexity of your passwords, the presence of a keylogger makes them ineffective. Regrettably, keyloggers continue to be a widespread threat, and they have not become obsolete as some may suggest. A recent post I came across in 2024 claimed that keyloggers are an outdated hacking tool. In reality, they remain a highly effective means of extracting sensitive information from a computer.
Example in Google Chrome
To see how the Google Chrome browsers stores login credentials, let us do a quick demonstration.
I start with going through the settings in Google Chrome. After that, I open an account in Tiktok. That means I have to create login credentials, and have Chrome create a complex password and store that with my login code.
Google Chrome settings
In chrome, click the three dots in the right top corner.
Scroll down to the bottom and click Settings
This will open a new tab with the Settings menu.
In the left pane, click Autofill and passwords.
Click Google Password Manager.
In the left pane, click Settings.
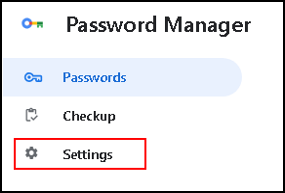
Here are the options to save passwords, and there is an option to sign in automatically. I activate both of them.
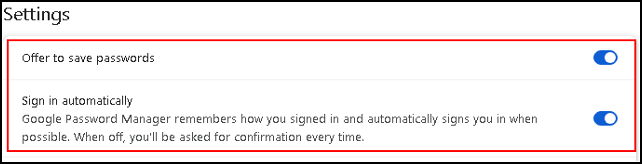
Use the buttons to activate, or deactivate.
This completes the settings in Google Chrome.
Create a new account with a password
Now that this is all set up correctly, I create a new Tiktok account and let Google Chrome create a new complex password. When I click the password field, a pop up appears that asks me if I need a suggestion for a strong password. Let me follow this suggestion.
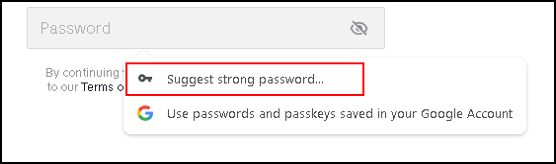
I click “Suggest strong password”.
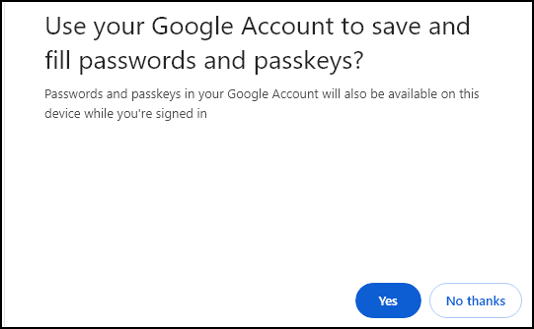
As you see, you can use your Google account to save passwords, I click Yes.
Now Google asks me for my password.

I enter my password and continue.
Now Google creates a new complex password for me.
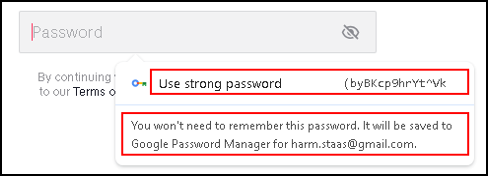
This is a long and complex password. Good that I do not need to remember it. This password is stored, and automatically retrieved when needed.
When you click “Use strong password”, the password is saved.
A message appears that the password is saved.
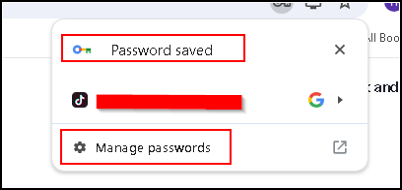
There is also an option to manage your password.
We go back to the password manager, and click Passwords.
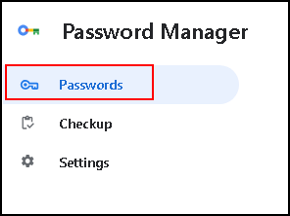
It shows the site I created the password for.
![]()
Now I want to see what happened, so I click tiktok.com..
I have to enter my password for my computer account.

And after entering my password.
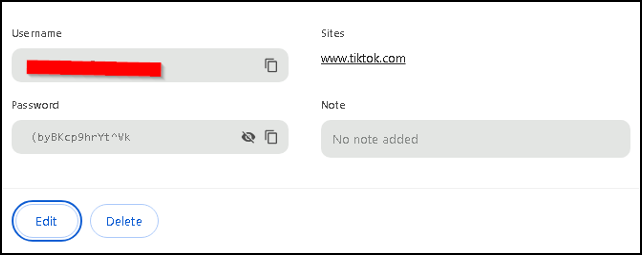
Now, when I go to the Tiktok web site, and click on the email address field, the following happens.
Google automatically filled in my login credentials for this web site. All I have to do is press the Login button.
Conclusion
It works, and that is great.
I can imagine that many people use this way of storing passwords. I would use this solution too if I have to go into a public space and use my laptop. It prevents me from having to enter my passwords manually. This is a far better solution then typing in passwords in a cafe or bus station. Are there people behind me looking at what I am typing? No problem. Is there a camera right on top of me? No problem. At least not for my passwords.
Would I use this at home? No. The only reason I would use this is in the above mentioned situation. When I am at home I would never use this. The simple question I ask myself, can I trust Google? What can they do with my passwords? I do not know, so I do not store them in Google.
This is the end of my post on browsers and passwords.
Disclaimer
All tips and methods mentioned in this blog are tested on Windows 11. Please note that results may vary on other operating systems or versions of Windows. Adapt the instructions accordingly.
Thank you for taking the time to read my post on browsers and passwords.
I hope you found it enjoyable and insightful.
Stay tuned for more content that is coming soon.
If you like what you read, please consider sharing it with others who might find it helpful.